Alopecia
Dermanext Hair Transplant (DHT)
Alopecia is a general term used to describe hair loss, which can manifest in various patterns depending on the underlying cause.
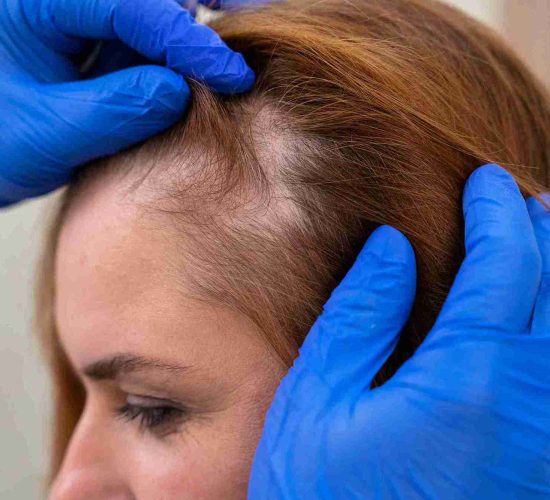
What is Alopecia?
Alopecia is a general term used to describe hair loss, which can manifest in various patterns depending on the underlying cause. The most common forms of alopecia include:
- Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks healthy hair follicles, leading to the development of round, smooth patches of hair loss. This condition can affect both the scalp and body.
- Physical or Emotional Stress: Stress can contribute to telogen effluvium, a temporary shedding condition.
- Androgenetic Alopecia: A hereditary condition also known as male or female pattern baldness. It typically causes thinning of hair along the scalp, often starting with receding hairlines or crown thinning.
- Telogen Effluvium: A condition where stress, illness, or major life events push hair follicles into a resting phase, causing excessive shedding. This is often temporary and resolves after the underlying cause is addressed.
- Scarring Alopecia: Inflammatory conditions like lichen planopilaris and lupus can damage the hair follicles, leading to permanent hair loss in the affected area.
When You See Bald Patches On Beard?
When you notice bald patches on your beard, it’s important to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis. A healthcare professional can perform diagnostic tests, such as a skin biopsy or blood tests, to determine the cause of the hair loss. Based on the results, they can recommend the most appropriate treatment options. Treatments like steroid injections or UV therapy should only be administered by certified medical professionals. It’s also crucial to address prolonged fungal infections with medical advice to prevent further complications.
How Long Does It Take for a Bald Spot to Regrow Hair?
The time required for hair regrowth in areas affected by alopecia varies depending on the severity of the condition. If you have a few small bald patches, hair may regrow completely within 6 to 12 months, sometimes without any treatment. However, it is not uncommon for bald patches to reappear in the beard.
What Causes Alopecia?
The causes of alopecia can range from genetic factors to medical conditions and environmental triggers. Some common causes include:
- Genetic Factors: Family history plays a significant role, particularly in androgenetic alopecia.
- Autoimmune Response: In alopecia areata, the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, menopause, and thyroid disorders can all impact hair growth cycles.
- Medications: Certain drugs, including chemotherapy agents, can induce hair loss.
- Physical or Emotional Stress: Stress can contribute to telogen effluvium, a temporary shedding condition.
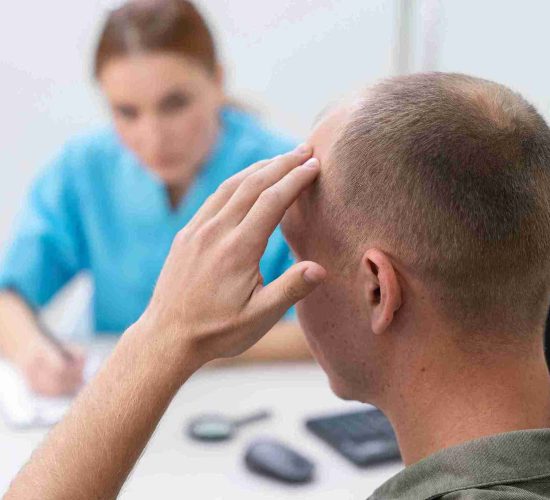
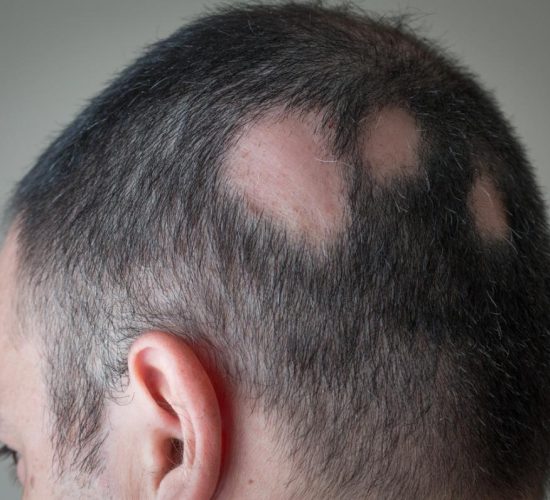

Treatment Options for Alopecia
While there is no single cure for alopecia, various treatment options can help manage the condition and promote hair regrowth:
- Topical Treatments: Minoxidil (Rogaine) is a popular topical treatment for androgenetic alopecia. It stimulates hair growth and may slow the progression of hair loss.
- Oral Medications: Finasteride (Propecia) is an FDA-approved medication that can help treat male-pattern baldness by blocking the hormone responsible for hair thinning.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In cases of alopecia areata, corticosteroids can be injected into the scalp to reduce inflammation and promote hair regrowth.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: This involves drawing a patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate platelets, and injecting it into areas of the scalp where hair thinning occurs. The growth factors in the plasma stimulate hair follicles.
- Hair Transplant Surgery: For individuals seeking permanent solutions, hair transplants can be performed to restore hair density by transplanting hair follicles from donor areas.
